MarCom & Sales
Legal
Legal factors have both an internal and external dimension to them. There are country specific laws and regulations that affect, or could impact if changed, the business environment in a specified country, while there are also certain policies that companies maintain for themselves (Codes of Conduct and alike). An in-depth legal analysis aims at answering both dimensions and then charts out the strategies in light of these legislations. Examples of legal factors include international selling laws, health and safety requirement, data protection (e.g., GDPR, CCPA and alike), competitive regulations, and employment laws.
Environmental
The last component of PESTLE analysis includes building understanding to environmental landscape. This dimension includes all those factors that influence or are determined by the surrounding environment. Environmental factors are more crucial for some industries than others. For example, tourism, farming, and agriculture are examples of industries that are heavily impacted by environmental factors. As a result of robust business environmental analysis, a firm should be able to detect factors such as climate, weather, geographical location, global changes in climate, and environmental offsets that will or can have an impact on the business. Understanding environmental issues in detail can also open up tremendous adjacent or new business opportunities.
Contact MarCom & Sales practice area to hear more how we can lead and facilitate your strategic marketing
Talk to usHow to analyze intensity of competitive rivalries?
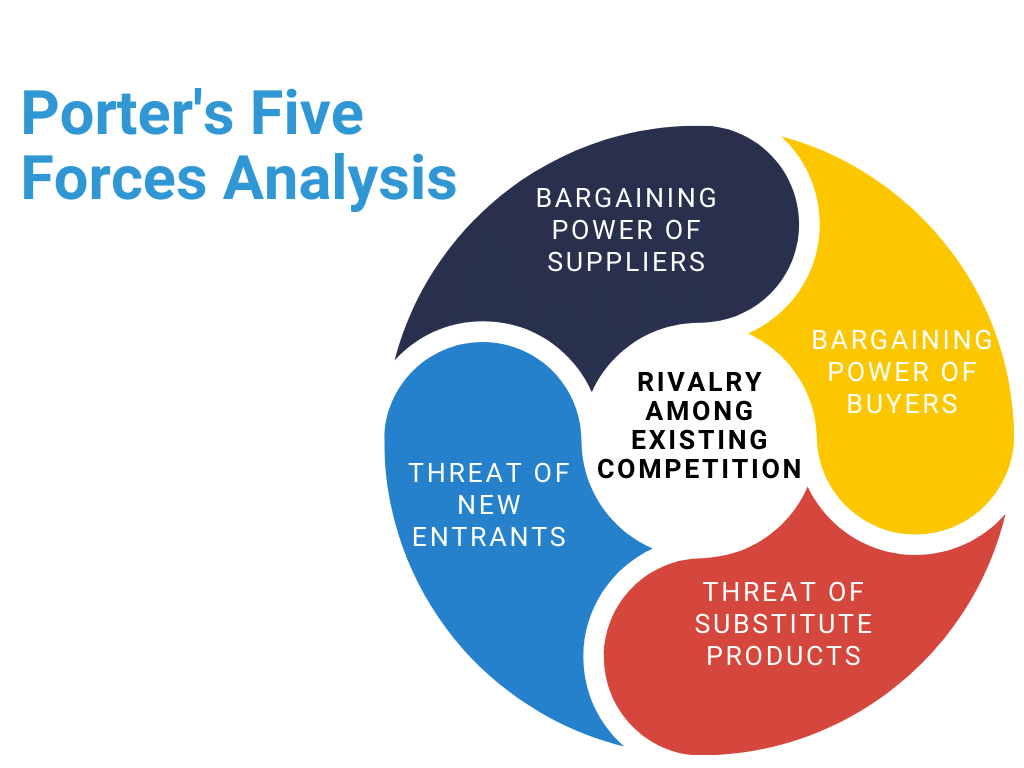
5-Forces analyses is another versatile tool that allows us to build transparency into intensity of competitive rivalry. 5-Forces analysis brings together four critical dimensions that together create and form the inputs of the competitive rivalry;
- Bargaining Power of Suppliers.
- Bargaining Power of Buyers.
- Threat of New Entrants.
- Threat of Substitute Products.
Intensity of competitive rivalry
Industry rivalry refers to the level or intensity of competition within a given industry. For example, if there are many firms with relatively small market shares divided among them then an industry is said to be competitive and possesses intense rivalry. Take for example the Global Sauna & Spa industry.
By contrast, an industry with a concentration of market shares in the hands of a few big producers is said to have lower rivalry and have more stable and less aggressive competition. Understanding the relative degree or intensity of rivalry gives us insights into the general methods that firms may use to gain an advantage over their competitors. It is important to note, any move that increases competition may spur other firms to react to meet these moves.
Some examples of competitive moves include: Price changes that give a competitor a temporary advantage with matching or better price. Differentiating product’s features and benefits to make it more attractive to the market. Innovating the method of distribution is another way competition seeks to gain an advantage. For example, this could be making the product available in different or more places, thereby making the product available to a larger market than it traditionally had been.
Remember, any competitive move made could be matched or bettered by competition which is why it is so difficult to sustain a competitive advantage over the long term, unless the competitive advantage includes “complex” system of activities that are hard to imitate by competition.
Factors that impact the intensity of competitive rivalry
Number of factors come to play that impact the intensity of rivalry. The below table indicates some of these based on various research streams and which we have encountered as part of our strategic marketing planning projects with various clients across industries;
- The number of firms in an industry competing for the same resources, customers and market.
- Slow growing markets tend to increase rivalry for similar reasons as when a market is served by many competitors.
- When costs to enter or do business are mostly fixed or unchanging this drives producers to increase production to capacity in order to reduce per unit costs. This process tends to increase supply and depress prices for the product or service being sold.
- If products are perishable this causes producers to all sell at the same time which depresses the price.
- If the products are commodities which are those types of products that are difficult for the market to differentiate the quality among competing offers.
- If the market is in a state of rapid change and there is the possibility of losing market share.
- Growing market and high profits are being made, this attracts new competitors to enter the market and attempt to claim a share of the growing market.
- If competing companies are highly diverse meaning, they have different corporate cultures and philosophies. Some might be very aggressive having more competitive corporate cultures that lead into increased risk taking and drive towards innovative breakthrough developments.
- An industry consists of a mix of old and new organizations where some are for example not-for-profit and others are for-profit enterprises.
Contact to learn more how our MarCom & Sales practice area can help your organization in strategic marketing
Talk to usInternal forces impacting marketing strategy
To a large degree organizations, regardless of the industry, have little, if any, ability to alter external forces of the marketplace. On the other hand, internal forces are those that an individual firm has lot of freedom and flexibility. Internal forces are those attributes of a given company that determine their capabilities to compete in a given market.
An understanding of the capabilities and deficiencies of a given organization is really no different than understanding oneself. Every person has talents, interests, and opportunities that they want to pursue. They also have areas where they are less talented than others and they are likely not interested in every opportunity that comes their way. The more clearly a person understand each of these attributes the better their chance of formulating operational strategies. Analyzing internal forces is much like a coach preparing the game-plan using various tools and frameworks, hence if effectively deployed, to understand internal forces better. It is important to note, in the short-term all forces are relatively fixed but in the long-term everything is variable.
To hear more about our toolkits and methodologies for strategic marketing, contact MarCom & Sales practice area
Talk to usCommunications – how to inspire action

The second dimension, communications, is an integral part of the MarCom & Sales triangle. The fundamental aspect of any well defined communications strategy is to inspire action – be that with internal or external stakeholders. An effective marketing strategy is the foundation for an effective communications strategy that defines how to deliver the intended key messages to the desired audiences at the right time.
Technological advancements impacting communications
Rapidly developing technologies (e.g., social media platforms like Facebook, Instagram, TikTok, Twitter, and YouTube) provide both opportunities and threats for communications. Today, more than ever, businesses are expected to be alert, reactive, responsive, and capable of managing their various stakeholders “round the clock.” Technology advancements ensure that customers and other stakeholders to large extent dictate the pace and timing of dialogue.